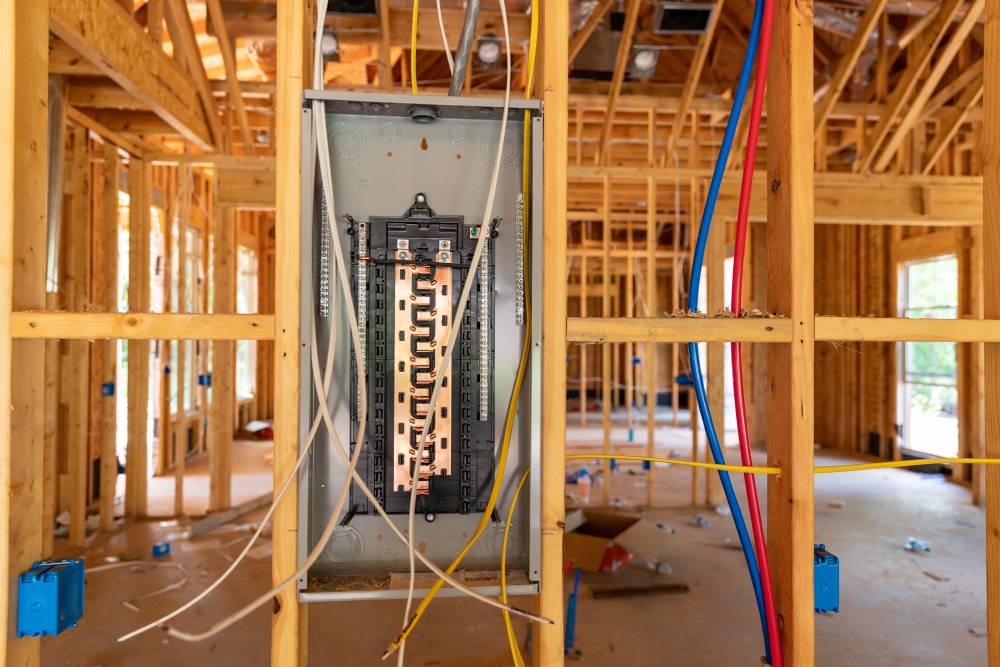
Understanding Circuit Breakers and Fuse Boxes
Circuit BreakersCircuit breakers are modern electrical safety devices found in most homes built after the 1960s. They are designed to automatically shut off electrical flow when an overload or short circuit occurs, preventing potential fires and electrical damage. Circuit breakers can be reset manually after they trip, making them convenient and reusable.
Fuse BoxesFuse boxes, found in older homes, serve a similar purpose but operate differently. Fuses contain a metal wire or filament that melts when the electrical current exceeds a safe level, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. Once a fuse blows, it must be replaced, making it a single-use device.
Components and Functionality
Components of a Circuit Breaker- Main Breaker: Controls the electrical supply to the entire house. It can shut off all electricity if necessary.
- Individual Circuit Breakers: Each breaker controls a specific circuit in your home, such as lighting, outlets, or major appliances.
- Bus Bars: Conduct electrical power to the individual circuit breakers.
- Grounding System: Provides a safe path for electricity to follow in case of a fault, preventing electrical shock.
- Main Fuse: Provides overcurrent protection for the entire electrical system.
- Individual Fuses: Each fuse protects a specific circuit within the home.
- Fuse Holders: Secure the fuses in place within the fuse box.
- Grounding System: Similar to circuit breakers, fuse boxes have a grounding system for safety.
When the electrical current in a circuit exceeds the breaker’s rating, it trips, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This can occur due to an overload (too many devices on one circuit) or a short circuit (a direct connection between the hot and neutral wires). To reset a tripped breaker, simply switch it off and then back on.
Fuse BoxesWhen a fuse blows, it means the metal wire inside has melted due to excessive current. This breaks the circuit and stops the electrical flow, preventing damage and potential fires. To restore power, you must replace the blown fuse with a new one of the same rating.
Join HICP Homeowner’s Alliance
Connect with experts, get special discounts and enjoy member benefits
Common Issues and How to Fix Them
Circuit Breaker Problems- Frequent Tripping: Often caused by overloaded circuits or faulty appliances. Distribute the load more evenly or unplug unnecessary devices.
- Loose Connections: Can cause arcing and fires. Ensure all connections are tight and secure.
- Old or Worn-Out Breakers: Replace aging or faulty breakers to maintain safety and functionality.
- Blown Fuses: Replace blown fuses with new ones of the same rating. Never use a higher-rated fuse, as this can cause overheating and fires.
- Corrosion: Clean or replace corroded fuse holders to ensure proper contact and prevent electrical faults.
- Insufficient Capacity: If your fuse box cannot handle your home’s electrical load, consider upgrading to a circuit breaker panel.
Upgrading from a Fuse Box to a Circuit Breaker Panel
Why Upgrade- Safety: Circuit breakers provide better protection against electrical hazards.
- Convenience: Circuit breakers can be reset, whereas fuses must be replaced.
- Capacity: Modern circuit breaker panels can handle higher electrical loads required by today’s appliances and devices.
- Consult a Professional: Hire a licensed electrician to assess your current system and determine the best upgrade options.
- Obtain Permits: Ensure all necessary permits are acquired before beginning work.
- Disconnect Power: The electrician will safely disconnect power to your home before starting the upgrade.
- Install the New Panel: The old fuse box will be removed, and the new circuit breaker panel will be installed.
- Connect Circuits: Each circuit will be connected to the appropriate breaker, and the system will be tested for proper operation.
- Inspection: A final inspection ensures the installation meets all safety codes and regulations.
Maintaining Your Circuit Breaker Panel or Fuse Box
Regular Inspections- Visual Checks: Inspect your panel or box for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Test Breakers: Periodically test your breakers to ensure they trip properly.
- Professional Inspection: Have a licensed electrician perform a thorough inspection every few years.
- Label Circuits: Clearly label each circuit in your panel or box for easy identification.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not overload circuits with too many appliances or devices.
- Use Proper Fuses: Only use fuses of the correct rating for each circuit.
- Keep Area Clear: Ensure the area around your panel or box is clear of obstructions for easy access.
Understanding the role and function of circuit breakers and fuse boxes is essential for maintaining the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. Regular inspections, proper maintenance, and timely upgrades can prevent many common electrical problems and ensure your home remains safe and functional. Always consult with a licensed electrician for any electrical work to ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your home and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a well-maintained electrical system.